9 Best Web Scraping Python Libraries for Beginners
Web scraping is the automated process of using software, or “bots,” to extract data from websites. It involves fetching web pages, parsing their HTML to find specific information, and storing the data for analysis, often in spreadsheets or databases. Common uses include market research, price comparison, and lead generation.
This beginner-friendly guide from 9Proxy introduces important Python libraries used for web scraping. From lightweight tools for basic tasks to advanced frameworks built for large-scale, dynamic scraping projects, this guide offers practical comparisons and expert tips to help match the right solution to any technical need. You will have a clear understanding of how to build stable, scalable scraping workflows using Python’s flexible ecosystem.

What Is Web Scraping In Python?
Web scraping in Python is the automated process of extracting data from websites using Python scripts. It involves fetching HTML content and parsing it to collect specific information like prices, reviews, or headlines. Python’s simple syntax and powerful libraries make it ideal for both beginners and advanced users working with static or dynamic web pages.

Many web scraping projects require handling both static pages and dynamic, JavaScript-rendered content. Python's versatility allows developers to choose the right tool for their specific needs, whether they're gathering product prices, tracking competitor changes, or collecting research data.
Top 9 Web Scraping Tools and Libraries
Urllib3
Urllib3 is a powerful HTTP client built into Python, ideal for basic scraping needs. If you need smooth control over your requests and prefer working with basic HTTP operations, Urllib3 is a great idea.
- Pros: It supports connection pooling, SSL verification, and proxy support. These features help make secure and efficient requests to websites.
- Cons: It doesn't parse HTML or JavaScript, so it's best paired with another tool like BeautifulSoup.
- When to Use? Use Urllib3 when you need low-level control over HTTP requests or need to fetch raw web data securely.

BeautifulSoup
BeautifulSoup is one of the most popular libraries for parsing HTML and XML content. This library transforms messy, real-world HTML into a navigable object structure, making it easy to find and extract specific elements.
- Pros: It has a simple API that helps you navigate and extract elements from messy HTML. It’s forgiving of errors and great for beginners.
- Cons: It’s slower compared to more robust frameworks like Scrapy when dealing with large-scale scraping.
- When to Use? Choose BeautifulSoup for small to medium scraping tasks where the focus is on parsing and extracting elements from static pages.

Requests
Requests stands as one of Python's most popular HTTP libraries due to its clean, simple API. This library makes sending HTTP requests straightforward by managing cookies, handling authentication, and processing redirects automatically. Requests abstracts away HTTP complexity, allowing developers to focus on their scraping logic rather than HTTP mechanics.
- Pros: Very easy to use, clean syntax, excellent documentation. It handles headers, cookies, and sessions efficiently.
- Cons: Like Urllib3, it doesn’t support JavaScript or parsing—so you’ll need another tool for that.
- When to Use? Combine Requests with BeautifulSoup or lxml for scraping static pages quickly.

MechanicalSoup
MechanicalSoup acts as a bridge between web browsers and Python scripts. This library provides high-level APIs to simulate human interactions with websites, including filling out forms, clicking buttons, and navigating pages. MechanicalSoup blends the best of Requests and BeautifulSoup to mimic basic browser interactions.
- Pros: Ideal for filling out forms, handling cookies, and navigating between pages. It feels like automating a real user session.
- Cons: Not designed for JavaScript-heavy sites; it's more suitable for simple interactions.
- When to Use? Use MechanicalSoup when your scraping requires simple form submissions or logins.

Selenium
Selenium is a powerful tool originally designed for browser automation and testing. It automates real web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Safari, allowing scripts to simulate genuine user actions, including clicking buttons, filling forms, and scrolling pages. This makes Selenium suitable for scraping JavaScript-heavy websites or applications with complex interactions.
- Pros: It interacts with JavaScript elements, simulates clicks, scrolls, and even handles file downloads.
- Cons: Heavier and slower than static methods. It also consumes more system resources.
- When to Use? Use Selenium when the website content is loaded dynamically with JavaScript.

Pandas
Pandas is a data analysis library that becomes valuable after you've extracted raw data. With its read_html() function, Pandas can directly parse HTML tables from web pages and convert them into structured DataFrames. Beyond scraping, Pandas excels at cleaning, transforming, and analyzing extracted data, making it essential for the post-scraping data processing stage.
- Pros: Allows powerful data manipulation and transformation. Works great for cleaning and analyzing scraped data.
- Cons: Doesn’t fetch data itself; used after scraping.
- When to Use? Use Pandas after scraping to format and export your data into CSV, Excel, or database formats.

ZenRows
ZenRows is a web scraping API that abstracts the complexity of anti-bot detection and proxy management. This service handles rotating proxies, CAPTCHA solving, JavaScript rendering, and anti-bot bypassing through a unified API.
- Pros: It automatically handles JavaScript rendering, rotating proxies, and anti-bot challenges.
- Cons: Limited free tier and may require a subscription for large-scale projects.
- When to Use? Perfect for production-level scraping where anti-bot measures are a concern.

Playwright
Playwright is a modern browser automation framework developed by Microsoft that supports multiple headless browsers (Chromium, Firefox, WebKit). Playwright handles dynamic content, complex interactions, and includes features like network interception and context isolation.
- Pros: Unlike Selenium, it loads pages faster and offers better support for modern JavaScript features.
- Cons: Slightly steeper learning curve for beginners.
- When to Use? Best suited for scraping modern, interactive websites that need JavaScript execution.

Scrapy
Scrapy is a web scraping framework built specifically for large-scale projects and professional use. This framework provides everything needed for web scraping, including built-in crawling, data extraction, storage, and middleware support.
- Pros: Built-in support for crawling, pipelines, and exporting data. Extremely fast and efficient.
- Cons: More complex to set up, and less beginner-friendly than BeautifulSoup or Requests.
- When to Use? Use Scrapy when you need to crawl multiple pages and manage large scraping projects.

How to Choose the Best Web Scraping Library?
Selecting the right tool depends on your specific requirements. Below is a comparison table to help you make a decision:
Depending on the complexity of your project, we at 9Proxy recommend starting with Requests + BeautifulSoup, and progressing to Playwright or Scrapy for more advanced needs. By the way, you can also choose based on your website type, project scale, and technical requirements to optimize your web scraping Python workflow.
To help with the scraping process, you might also want to explore nstbrowser, which provides valuable insights into how to automate the browsing process.
Use Cases Of Web Scraping In Python
Python web scraping isn’t just for developers; it’s a practical solution for anyone needing large-scale web data collection. Here are some common use cases where web scraping in Python can bring real value:
- Competitor Analysis: Track changes in pricing, product offerings, and content strategies on competitor websites to stay ahead in your market.
- Price Comparison: Collect price data from multiple e-commerce platforms to offer the best deals or monitor pricing trends.
- Lead Generation: Extract contact details (like emails or phone numbers) from public directories or business listings to build prospect lists. This is really effective when paired with a linkedin web scraper to target professional leads.
- Sentiment Analysis: Gather customer reviews or social media posts to analyze public opinion about a product, brand, or event.
- Social Media Analytics: Scrape user engagement data, hashtags, or trends from platforms like Reddit, Twitter, or Instagram.
- Research & Journalism: Collect structured data for academic research or monitor breaking news and public data sources.
These examples show how Python web data scraping can support both business intelligence and content strategy.
Step-by-step Guide to Building A Web Scraper In Python
Now that you understand what you can do with it, let’s break down how to actually build a working scraper. We'll walk you through key steps, from setup to troubleshooting.
Setting Up for Web Scraping
Before writing any code, you need to prepare your working environment:
- Install Python 3 and ensure it's added to your system PATH.
- Create a virtual environment using venv or virtualenv to manage dependencies.
- Install required libraries, such as:
pip install requests beautifulsoup4 scrapy selenium pandas

This setup ensures your scraper runs smoothly and avoids conflicts between projects.
Working on Scraping Process
Building a scraper involves several clear steps. Here's how we do it:
Step 1: Identify the target data Step 2: Make an HTTP request import requests response = requests.get("https://example.com") In some cases, especially when downloading resources or dealing with command-line tools, developers may also use wget proxy configurations to route requests securely through a proxy Step 3: Parse the content from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser') Step 4: Extract specific elements titles = soup.find_all("h2", class_="title") Step 5: Store the data import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame(titles) df.to_csv("output.csv", index=False) Step 6: Add logic to scrape multiple pages With this workflow, even large sites can be scraped methodically with clean, repeatable code. import time from requests.exceptions import RequestException try: response = requests.get(url) except RequestException: time.sleep(5) # retry logic here Proxies are especially useful for scaling scraping tasks while avoiding bans or CAPTCHA. Web scraping in Python offers a flexible, scalable way to extract data across the web. With beginner-friendly libraries like Requests and BeautifulSoup, and advanced tools like Playwright or Scrapy, you can scrape anything from a blog to a dynamic e-commerce platform. At 9Proxy, we believe using proxies is key to keeping your scrapers running smoothly and safely. Whether you're comparing prices, collecting leads, or analyzing sentiment, choose the right tools and the right proxies for the job.
Use your browser’s "Inspect" tool to find where the data lives on the page, whether it’s inside a 
Use requests to fetch the page:
Use BeautifulSoup to turn the HTML into something you can work with:
Use .find() or .find_all() to get the data:
Save to CSV using Python’s built-in csv module or pandas:
Use loops or recursion to handle pagination or load more buttons.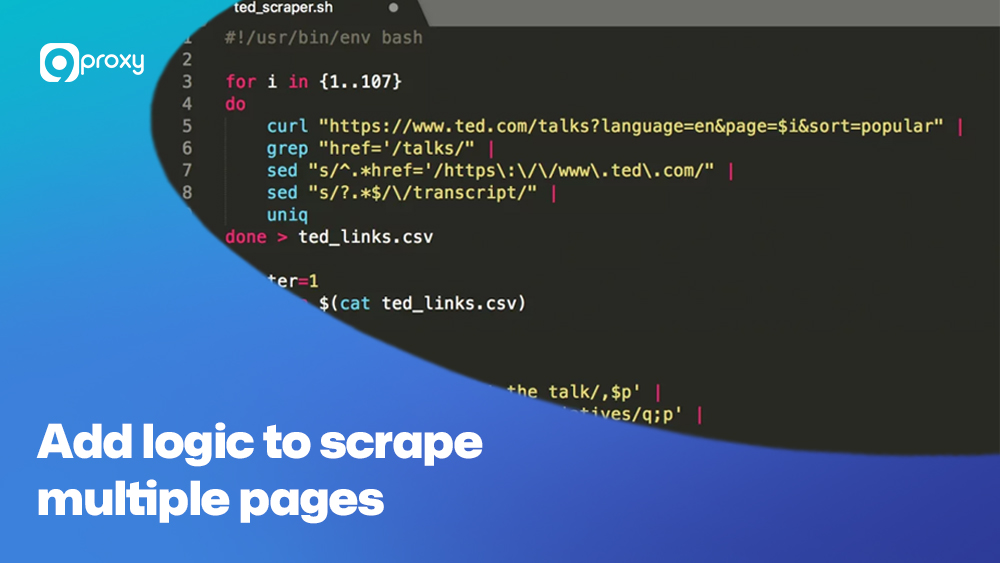
Deal with Common Issues in Web Scraping Python
Handling errors and timeouts
Web scraping often runs into broken connections, 403 errors, or timeouts. Use try/except blocks, retry logic, and time delays to improve stability: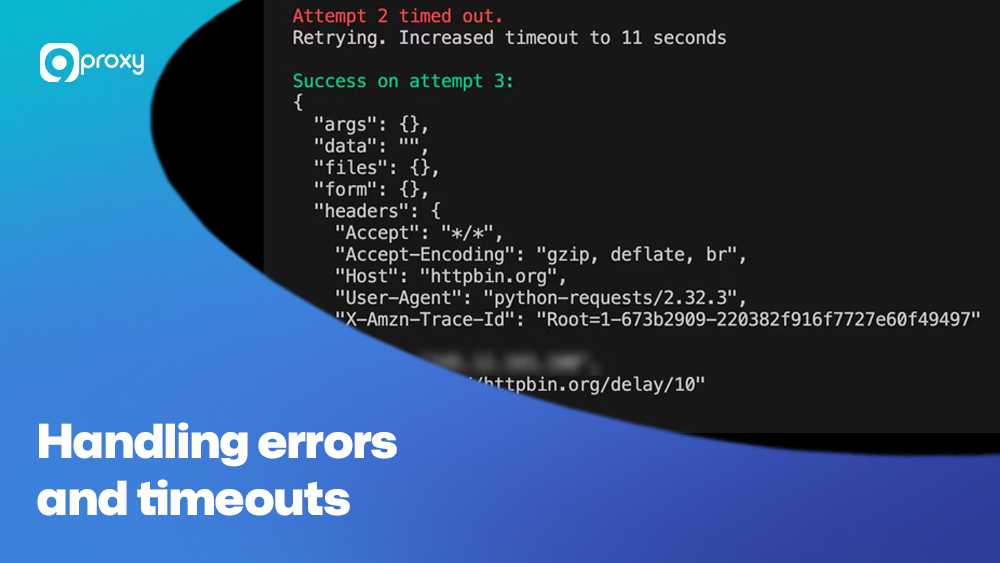
Avoiding IP blocking
Many websites detect and block scrapers. To stay undetected:Conclusion
Get Newsletters About Everything Proxy-Related