What is a Reverse Proxy Server? Easy Setup Guide for 2025
Looking to improve website performance, security, and flexibility? A reverse proxy server might be just what you need. In today’s digital landscape, fast and secure access to online services is essential. A reverse proxy server sits between your users and backend services, acting as a smart intermediary to manage traffic, boost speed, strengthen security, and handle SSL encryption.
9Proxy will walk you through what a reverse proxy server is, why it matters, the benefits it brings, and how to set it up in just a few steps. By the end of this guide, you'll know exactly how to set up a reverse proxy server to make your website faster, safer, and easier to manage.
What Is a Reverse Proxy Server?
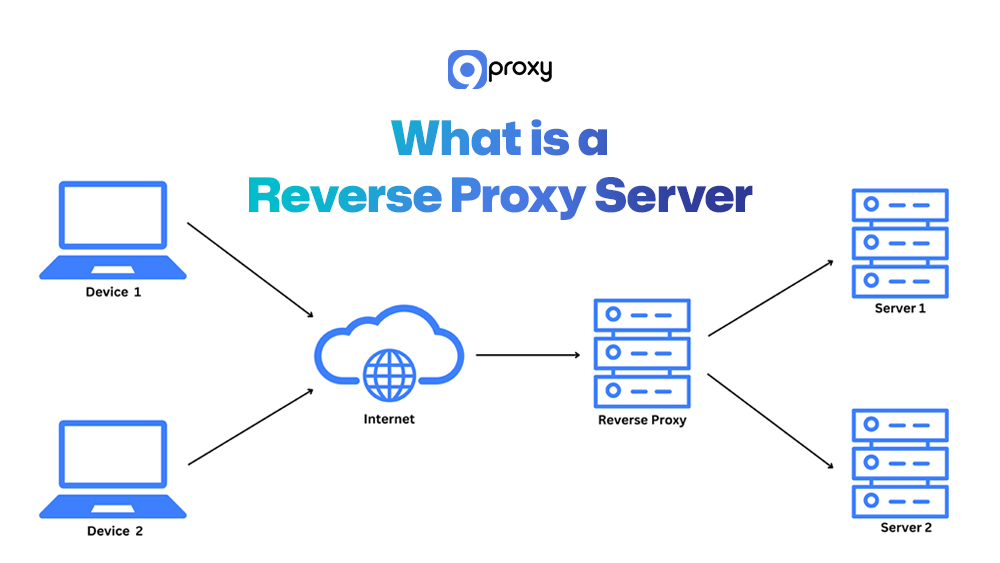
A reverse proxy server is a gateway that sits between users and your backend servers. Instead of users connecting directly to your origin servers, their requests first go through the reverse proxy. It then forwards those requests to the right backend server, receives the response, and sends it back to the user.
This setup helps hide your internal infrastructure, manage traffic, improve speed, and boost security. In modern web architecture, a reverse proxy server also handles tasks like SSL encryption, load balancing, caching, and filtering unwanted traffic—making your website faster, safer, and more reliable.
Types of Reverse Proxies
Organizations choose different types of reverse proxy servers based on their setup and goals. Understanding these types helps you pick the right solution.
Software-based Reverse Proxies
These run as applications on servers or in the cloud (e.g., Nginx, HAProxy, Apache). They are flexible, easy to update, and ideal for scaling as traffic grows. In some setups, understanding the difference between static vs rotating proxies is also important, especially when optimizing traffic distribution and IP rotation for performance and anonymity.
Hardware-based Reverse Proxies
These are physical devices often used in enterprise environments. They offer high performance and built-in features, but require physical setup and maintenance.
Load Balancing Reverse Proxies
These distribute traffic across multiple backend servers to avoid overload. They improve uptime by redirecting traffic if a server fails.
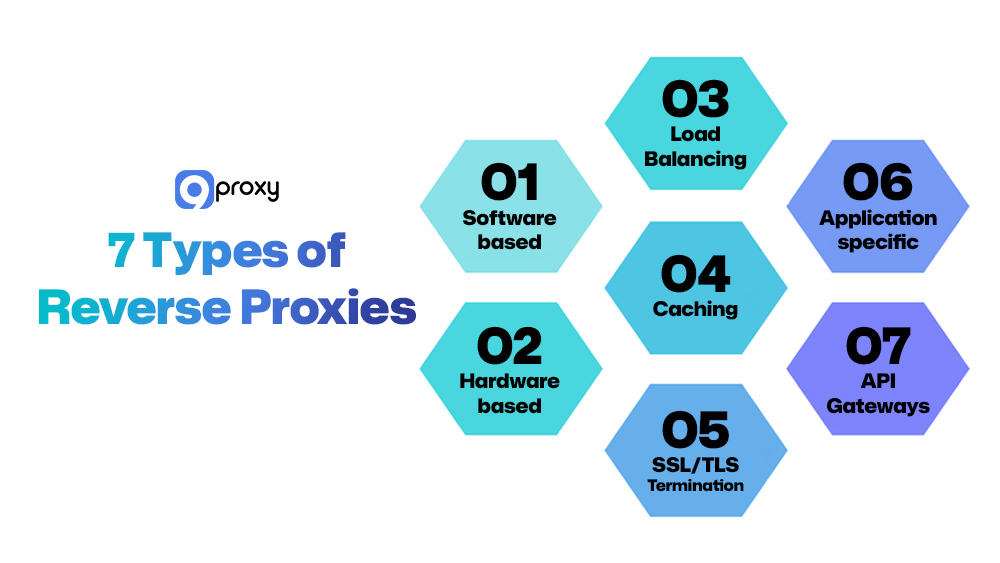
Caching Reverse Proxies
These store copies of static content like images or pages to serve users faster and reduce the load on backend servers.
SSL/TLS Termination Reverse Proxies
These handle HTTPS encryption and decryption, reducing workload on backend servers and centralizing security tasks.
Application-specific Reverse Proxies
Tailored for certain protocols such as HTTP, WebSocket, or FTP, these proxies offer settings optimized for specific use cases.
API Gateways
Act as reverse proxies for API traffic. They manage authentication, rate limiting, routing, and version control to make API infrastructure more secure and efficient.
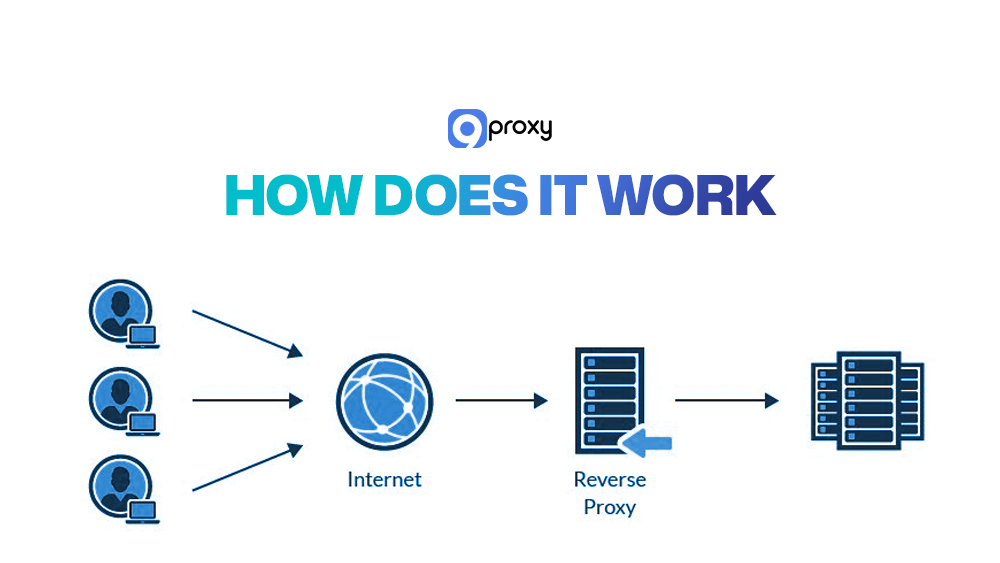
How Does a Reverse Proxy Work?
Understanding how a reverse proxy works makes setup and troubleshooting easier. When a user visits your site, their request first goes to the reverse proxy instead of directly to your backend servers. The proxy checks the request and decides which backend server should handle it based on your settings.
Before forwarding the request, the reverse proxy can modify it, such as adding headers, changing URL paths, or applying security filters. Then it sends the request to the chosen server.
After the backend server processes the request, the response returns through the reverse proxy. The proxy may compress the data, add caching headers, remove sensitive information, or log performance data before delivering the response to the user. Users only experience a smooth interaction without seeing the internal server infrastructure.
Benefits of Reverse Proxy
A reverse proxy brings many useful benefits to websites and online systems. It helps websites run faster, stay more secure, and be easier to manage. It also keeps your site online even if one of your servers goes down. Here are the main advantages of using a reverse proxy:
- Faster Performance: Speeds up websites by caching content and sharing traffic across multiple servers.
- Better Security: Hides your real servers, blocks harmful requests, and manages SSL certificates safely.
Easier Management: Lets you control traffic rules and security settings from one central place. - Higher Reliability: Keeps your site available by sending users to a working server if another one fails.
Common Use Cases of a Reverse Proxy Server
Reverse proxy servers help solve key challenges in website performance, security, and reliability. Businesses use them to manage traffic, protect internal systems, and improve user experience. While many wonder why use proxy instead of vpn for privacy or routing purposes, a reverse proxy focuses more on web traffic management, caching, and secure delivery for websites and APIs.
- Load balancing: A reverse proxy distributes traffic across multiple servers so no single server gets overwhelmed. This keeps your website fast, even during traffic spikes.
- Protecting backend services: The reverse proxy hides your origin servers from the public, making it harder for attackers to find and exploit them. It acts as a security shield for your infrastructure.
- Content delivery optimization: Reverse proxies speed up websites by compressing data and caching frequently accessed content. This reduces load times and improves performance for users everywhere.
- Caching static assets: Files like images, CSS, and JavaScript are served instantly from the proxy’s cache. This lightens backend load and delivers faster page responses.
- SSL/TLS offloading: The reverse proxy handles HTTPS encryption so backend servers can focus on core tasks. This reduces CPU usage and improves overall speed.
- API gateway management: API traffic passes through the reverse proxy, where rate limits, authentication, and access policies are enforced in one central place.
- Secure remote access: Employees can use internal apps securely from anywhere. The reverse proxy controls access, reducing exposure to the public internet.

Step-by-Step: How to Set Up a Reverse Proxy Server?
Setting up a reverse proxy server includes five main steps: choosing software, installing it, configuring settings, enabling SSL, and testing the setup. Follow these steps in order for a smooth and secure deployment.
Step 1: Choose Your Reverse Proxy Software
Select software that fits your infrastructure:
Nginx: Lightweight, fast, ideal for general use, and handles many connections efficiently.
HAProxy: Best for advanced load balancing and high availability.
Apache: Great if you're already using Apache, with mod_proxy modules.
Choose based on performance needs, expected traffic, existing tools, and SSL support. If you're already using Nginx or Apache, adding reverse proxy functionality requires minimal setup.

Step 2: Install the Software
Use your system's package manager:
Nginx:
sudo apt install nginx # Ubuntu/Debian
sudo yum install nginx # RHEL-based
HAProxy:
sudo apt install haproxy
sudo yum install haproxy
Apache:
sudo apt install apache2
sudo yum install httpd
sudo a2enmod proxy proxy_http # Enable proxy modules
sudo systemctl restart apache2
After installing, check the service status to ensure it’s running:
sudo systemctl status nginx | haproxy | apache2

Step 3: Configure the Reverse Proxy
Each tool has different configuration files:
Nginx:
Edit: /etc/nginx/sites-available/yourdomain.conf
Key directives:
proxy_pass http://backend:8080;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
HAProxy:
Edit: /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
Define frontend/backend, example:
frontend http_front
bind *:80
default_backend http_back
backend http_back
server web1 192.168.1.10:8080
Apache:
Edit: /etc/apache2/sites-available/yourdomain.conf
Add:
ProxyPreserveHost On
ProxyPass / http://backend:8080/
ProxyPassReverse / http://backend:8080/
Validate your config before restarting:
sudo nginx -t
sudo haproxy -c -f /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
sudo apache2ctl configtest
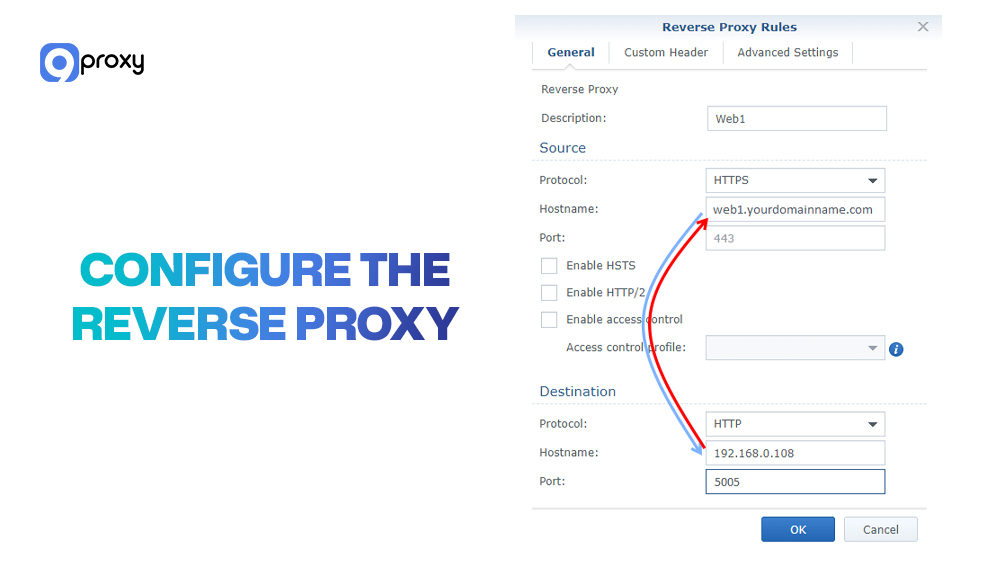
Step 4: Add SSL with Let’s Encrypt (Optional but Recommended)
Using SSL/TLS protects user data. Let’s Encrypt offers free certificates. Install Certbot:
For Nginx/Apache:
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-nginx
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-apache
For HAProxy:
sudo apt install certbot
Request a certificate: sudo certbot certonly --standalone -d yourdomain.com
Configure redirection to force HTTPS:
Nginx:
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
Apache: Use Redirect or RewriteRule.
HAProxy: Bind both HTTP and HTTPS, then redirect HTTP to HTTPS. Enable auto-renewal: sudo systemctl enable certbot.timer
During this process, ensure proper DNS configuration and domain mapping to avoid connection issues. Using a guide on proxy server dns can help you verify that your proxy and backend servers resolve correctly under SSL.

Step 5: Test the Configuration
Verify your reverse proxy server works correctly:
Browser test: Visit your site to ensure it loads over HTTPS.
Curl test: curl -I https://yourdomain.com
- Check for correct headers like X-Real-IP and SSL validity.
- Check logs on backend servers to ensure client IPs are forwarded correctly.
- SSL validation: Use browser security indicators or test with SSL Labs.
Make sure all pages, logins, and features work without errors. Fix header or SSL issues before going live.
Reverse Proxy Software Compared (2025)
Different reverse proxy solutions offer unique strengths depending on your needs, technical setup, and team experience. This comparison helps you choose the right tool for your environment.
Some software is better for high-traffic sites, others for container-based setups or quick SSL deployment. Knowing their differences makes it easier to select the right one.
Tips to choose:
- Use Nginx if you want a reliable all-rounder with a big support community.
- Pick HAProxy for advanced load balancing and detailed monitoring.
- Choose Apache if your team already uses it, easy to integrate.
- Go with Caddy for simple projects needing instant HTTPS.
- Select Traefik if you're running apps in Docker or Kubernetes.
Match your decision with your team’s expertise. Start simple, scale as needed, and document your choice for future maintenance.
Pros and Cons of Using Reverse Proxy Software
Before setting up a reverse proxy server, it’s important to understand both the advantages and disadvantages. This tool can greatly improve your website’s speed, security, and manageability, but it also adds complexity. Knowing the pros and cons will help you decide if it’s the right choice for your system and team.
Pros of Reverse Proxy Server
Better performance and faster speed
A reverse proxy server can cache static files like images and scripts, so users don’t need to request them from the backend every time. It can also compress data before sending it, and balance traffic across multiple servers. This helps reduce loading times and prevents any one server from being overloaded.
Stronger security
The reverse proxy hides your backend servers from the public, making them harder to attack. It can block harmful requests before they reach your internal network and handle SSL encryption to protect user data. In some corporate setups, similar security layers are used for internal communications, like an email proxy server to protect email traffic and filter malicious messages before reaching internal mail servers.
High availability and uptime
If one of your servers goes down or needs maintenance, the reverse proxy can automatically redirect traffic to another server. This keeps your site online even during problems, so users don’t experience errors.
Central control of settings
With a reverse proxy, you can manage SSL certificates, traffic rules, and security settings in one place. This saves time and keeps everything consistent across your system.

Cons of Reverse Proxy Server
More complexity to manage
A reverse proxy adds another part to your system that needs setup, monitoring, and troubleshooting. If something goes wrong, it might be harder to find the problem. Your team will need to understand how it works.
Slight delay in response time
Every user request passes through the proxy, which adds a small delay (usually 1 to 5 milliseconds). If the proxy is not properly configured or is low on resources, it can slow things down more than expected.
Single point of failure risk
If the reverse proxy stops working, all access to your backend servers is lost, even if they are running fine. To avoid this, you may need a backup proxy or load-balancing setup, which adds cost and setup time.

Troubleshoot Common Issues
When using a reverse proxy, technical issues may occur. Knowing how to detect and fix these problems helps maintain stable performance and prevents user frustration. Below are the most common issues and how to solve them.
502/504 Gateway Errors
These happen when the reverse proxy can't reach a backend server or the server responds too slowly.
- Check if backend servers are online and reachable.
- Use tools like ping, curl, or telnet to test connections.
- Verify backend IP addresses and ports in your proxy config.
- Review proxy and server logs for timeouts or connection errors.
- Increase timeout values if needed.
- Monitor server resources like CPU and memory.
In some hybrid setups involving data protection systems like veeam backup proxy, connection bottlenecks may appear due to simultaneous data transfers or backup jobs passing through the proxy layer.

Incorrect Header Forwarding
Some applications need specific headers like client IP or protocol type.
- Ensure these headers are included: Host, X-Real-IP, X-Forwarded-For, X-Forwarded-Proto.
- Use curl -v to test and view sent headers.
- Check backend logs to confirm they receive the right headers.
- Add custom headers if your app requires them.
High Resource Usage
A reverse proxy under heavy load may slow down or crash.
- Monitor CPU and memory with tools like top or cloud dashboards.
- Tune settings like worker_connections (for Nginx).
- Limit excessive caching or buffer sizes.
- Upgrade server hardware if needed.
SSL Misconfiguration
Improper SSL settings can cause browser warnings or connection failures.
- Make sure SSL certificates are valid and not expired.
- Use SSL Labs to test your config.
- Check permissions on private key files.
- Ensure full certificate chains are installed.
- Disable weak ciphers and use secure ones.
- Test with: curl -v https://yourdomain.com
Backend Compatibility Issues
Some apps don’t work well behind a proxy without extra configuration.
- Pass the client IP with forwarding headers.
- Ensure Host headers are preserved.
- Test all features after setup.
- Note any app-specific issues and apply workarounds.
- Some legacy apps may need special proxy rules..

Conclusion
A reverse proxy server is a key part of modern web systems. It boosts performance, improves security, and helps your site stay reliable. By sitting between users and backend servers, it balances traffic, hides internal systems, caches content, handles SSL, and blocks harmful requests. We've covered how reverse proxies work, how to set one up, and which tools to choose, like Nginx, HAProxy, or Apache. Setting up a reverse proxy reduces load, prevents downtime, and improves user experience. Take the next step today with 9Proxy‘s proxy products and build a powerful, scalable web infrastructure that drives your growth and gives your customers the fast, secure experience they expect.
Get Newsletters About Everything Proxy-Related